Vermont EPSCoR's Streams Project; A Teacher Collaboration on WikiEducator
Openly shared content, practices, and developing resources from Vermont EPSCoR's Streams Project. Join this collaboration and make a difference!
 East Orange Branch |
|---|
|
| Stream code: | CTWW_EOBrnch_1567 |
| Basin: | Upper Connecticut - Mascoma |
| State or Province: | Vermont |
| Country: | USA |
| Latitude: | 44.0769 |
| Longitude: | -72.37151 |
| School: | Oxbow High School |
The following are the most common invertebrates collected from this stream site.
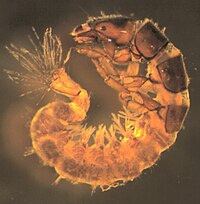
Baetis
- Order
- Ephemeroptera
- Family
- Baetidae
- Genus
- Baetis
- Common name
- The Little Olive
- Tied fly
- Sawyer Pheasant Tail Nymph
This mayfly has three "tails" and a unique head shape. Its gills are oval shaped and insert dorsally. More mature nymphs have long, dark wing pads.
Image of the long, dark wing pads.
Simuliidae
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Simuliidae
Simuliidae appear rather like bowling pins with heads. Relatively speaking, we collect few members of this family and have we have not identified them past family at this point.
Click here for a close up image of the heads.
Glossosomatidae
- Order
- Trichoptera
- Family
- Glossosomatidae
- Common name
- saddlecase caddisfly
Larvae in this family build domed cases made of small rocks, and are often wider at segment 5. The pronotum is covered in dark, sclerotized plates, but there are either
no sclerites on the mesonotum, or the mesonotum is unsclerotized with the exception of a few patches. The anal proleg is broadly joined to segment 9; the anal claw has one or more accessory hooks. The
pronotal excision is small (approximately 1/3 anterolaterally) to accommodate the coxae.
Commonly encountered genera include Glossosoma and Agapetus.
Epeorus
- Order
- Ephemeroptera
- Family
- Heptageniidae
- Genus
- Epeorus
- Common name
- The Quill Gordon
- Tied fly
- Quill Gordon
This is the only Heptageniidae genus present in this area with two tails!
Hydropsychidae
- Order
- Trichoptera (caddisfly)
- Family
- Hydropsychidae
- Common name
- net spinning caddisfly
- Tied fly
- Emergent Sparkle Pupa, Vermont Hare's Ear
This family of net-spinning caddisflies is very abundant at several sites. They are important filtering collectors and are quite common at urban and agricultural sites where particles of organic material can be important food resources. Genus-level identification is possible for mature specimens and we will include the genera we found at your site if possible.
When using the key, some features that are challenging to see are the forked trochantin and the paired sclerites in the folds between segments. Other, more easily seen key features include filamentous gills on the abdominal segments and the sclerotization of the dorsal surfaces of all three thoracic segments. Keep in mind that with smaller or more immature specimens, genus-level ID may not be possible.
Commonly found genera include Cheumatopsyche, Ceratopsyche, and Hydropsyche. Less commonly, we have found Arctopsyche and Potamyia.
Images of the forked trochantin and the paired sclerites.
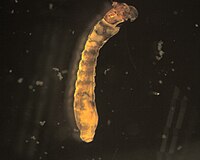
Chironomidae
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Chironomidae
- Common name
- Nonbiting midge
- Tied fly
- Griffith's Gnat
Midge larvae tend to be the most common macroinvertebrate at our sites. As with other Diptera, there are no true jointed legs. Chironomidae do have a pair of prolegs at each end and preserved individuals tend to curl into a 'C'. Identification past family requires slide-mounted heads. We have seen philopotamid caddisflies misidentified with the chironomids and we suspect that that happens when samples are being sorted from trays. Under a microscope, six prominent legs can be seen on members of the caddisfly family Philopotamidae.
More information on Philopotamidae.
Perlodidae
- Order
- Plecoptera
- Family
- Perlodidae
Stoneflies in the Perlodidae family do not have branching gills from leg bases. When observing their mouthparts, the glossae and paraglossae form a large three-pronged notch, or opening. The hind wing pads are divergent. Cerci, or "tails," are as long or longer than the abdomen.
Images of mouthparts, thehind wing pads and the ventral view.
Athericidae
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Athericidae
- Common name
- water snipe flies
Members of the family Athericidae have wrinkled bodies with prolegs on the ventral side. Their mandibles- which can be seen by carefully cutting the head open- move parallel to each other. On the end of their abdomen there are two lobes fringed with setae. Our collections include just the single genus Atherix.
Image of the two lobes of the abdomen.
Chloroperlidae
- Order
- Plecoptera
- Family
- Chloroperlidae
- Common name
- The Yellow Sally
- Tied fly
- Yellow Sally
Stoneflies from the family Chloroperlidae have cylindrical banded abdomens. When observing their mouthparts, the glossae and paraglossae form a three-pronged (open) notch, and their hind wing pads are parallel (not divergent). Cerci have a vertical fringe of hairs pointing away from the abdomen. Setae on the pronotum are found primarily at the corners.
Peltoperlidae
- Order
- Plecoptera
- Family
- Peltoperlidae
- Common name
- The Little Roach-like Stonefly
- Tied fly
- Yellow Humpy
Peltoperlidae have stout, roach-like bodies and can have conical gills at the base of legs. Ventral overlapping plates are found on their large thorax. They have a single gill on each side posterior to thoracic segment 3. Peltoperlidae is not covered in the family-level key (Bouchard 2006) used by the Streams Project.
Image of the single gill on each side posterior to thoracic segment 3.
Ephemerellidae
- Order
- Ephemeroptera
- Family
- Ephemerellidae
- Common name
- spiny crawler mayflies
- Tied fly
- Blue-Winged Olive
The mayfly
Ephemerellidae is distinguished by the absence of gills on the second abdominal segment; individuals either have gills on segments 3-7 or 4-7. Some may have operculate (plate-like) gills on the fourth segment, though in many the gills are of identical size. The most commonly found genera include
Drunella,
Ephemerella, and
Serratella.
More information on the genera Drunella, Ephemerella, and Serratella.
Dolophilodes
- Order
- Trichoptera
- Family
- Philopotamidae
- Genus
- Dolophilodes
Maccaffertium
- Order
- Ephemeroptera
- Family
- Heptageniidae
- Genus
- Maccaffertium
- Common name
- The March Brown
- Tied fly
- March Brown
This genus of
Heptageniidae is distinguished by its gills on the seventh abdominal segment, which are reduced to slender filaments. Gills on segments 1-6 are truncated.
Images of the slender filaments, and the truncated gills.
Pteronarcys
- Order
- Plecoptera
- Family
- Pteronarcyidae
- Genus
- Pteronarcys
- Common name
- The Giant Stonefly
- Tied fly
- Kaufmann's Black Stone
Pteronarcyidae have branching gills from the bases of their legs as does
Perlidae. What distinguishes Pteronarcyidae from Perlidae is the presence of gills on the first two abdominal segments. There are only two genera in this family, but the other,
Pteronarcella, is only found in the west/southwest.
Click to see an example of Perlidae or the gills on the first two abdominal segments.
Elmidae
- Order
- Coleoptera
- Family
- Elmidae
- Common name
- riffle beetle
We very commonly find adult and larval riffle beetles. The adults are clearly beetles, but the larvae can be confused with other orders. The forward pointing tooth on the front end of the larvae as described in the key can be a challenge to see, particularly in small individuals. Larvae are characterized by having a single tarsal claw at the end of their legs, which have 4 segments. Adults, on the other hand, have two tarsal claws at the end of each leg. Commonly encountered genera include
Dubiraphia,
Macroychu,
Optioservus,
Phanocerus,
Promoresia, and
Stenelmis.
Images of the adult and larval riffle beetles.
More information on Dubiraphia, Macronychus, Optioservus, Phanocerus, Promoresia, and Stenelmis.